Unraveled: the composition of steel wire ropes – and why it matters
Are you involved in choosing a new steel wire rope? Then you will be faced with an endless number of options. The composition of a steel wire rope in combination with its application largely determines the life span of the steel wire rope. Discover how a steel wire rope is constructed and how this can affect its performance.
If we look at the construction of a steel wire rope, there are many possible variations. The number of strands, the number of wires, the structure of those wires in the strands, the finish of the wire rope, the choice of material, and the method of striking can vary greatly from one construction to another.
Steel wire ropes consist of several fixed opponents:
- A core
- Strands (core wire, inner and outer wires)
What function does each component have, what variations are possible and how do these aspects affect the steel wire rope? We list the most important points.
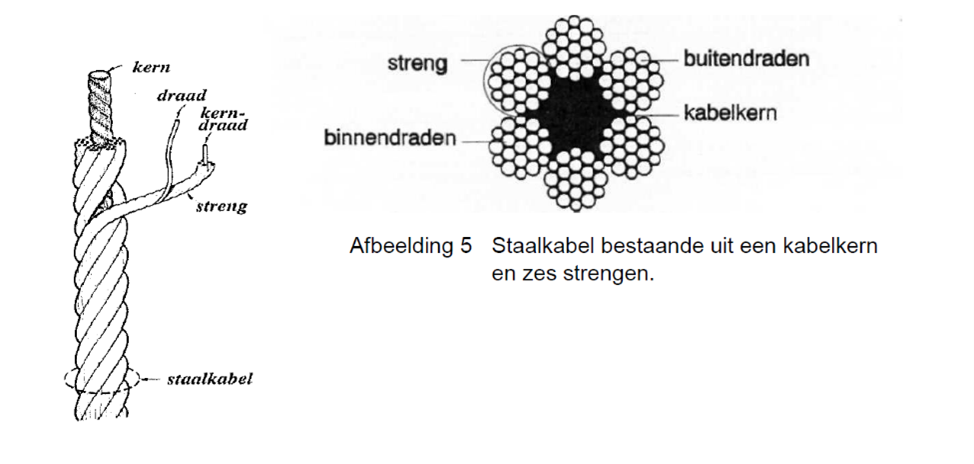
The Core
The core wire is the heart of the wire and ensures an even distribution of the different strands around the core wire. The core prevents the strands from bearing on each other with great force, which makes bending difficult and causes tension in the steel wire rope to become too high.
Materials
A core wire can be made of rope, synthetic fiber or steel.
Rope
At first glance, a rope core seems to have beneficial properties. In the past, people were also convinced of this. Nevertheless, caution is needed because a rope core also has many disadvantages when used.
Advantages:
- The strands move easily over the tope core when bent, without damaging or wearing out the wires.
- No intersections occur between the rope core and the strands, which allows for wear and tear.
Disadvantages:
- Becomes thinner over time, causing the strands to come together. This leads to wear, which you can’t see from the outside.
- With use, the wire rope lubricant is squeezed out of the core. Eventually the core absorbs moisture, resulting in corrosion.
- The flexibility of the rope core is quickly lost after use.
- Ages and decomposes quickly and burns with heat.
- Hard to obtain nowadays.
Synthetic fiber
Synthetic fiber cores are particularly suitable for elevator ropes and the fishing industry. Again, caution is advised: synthetic fiber cores have the same disadvantages as rope cores (except that synthetic fiber is readily available).
Advantages:
- A rope with a synthetic fiber core is more elastic than steel and rope.
- Does not rot.
- More flexible than steel.
- Does not absorb moisture, does not rust.
Disadvantages:
- Same disadvantages as a rope core, except that a synthetic fiber core is easy to obtain.
- Does not increase the breaking load of a wire rope (while a steel core does).
Steel
Compared to rope and synthetic fiber, a steel core has the most advantageous properties.
Advantages:
- Provides support and an even distribution of strands.
- Not compressible
- More abrasion resistant than rope and synthetic fiber.
- Provides permanent elastic stretch to the steel wire rope.
- Increases resistance to deformation.
- Resistant to corrosion: the rope lubricant is not squeezed out of the core when used.
- Increases the breaking load of the wire rope.
Disadvantages:
- Less flexible than rope or synthetic fiber.
Strands of a steel wire rope
Around the core wire are the strands. A strand consists of an x-number of steel wires, which are wound helically around the core strand. The number of strands varies from one wire rope to another, but by far most steel wire ropes consist of six strands.
Lay method
The strands are closed around the core wire in a certain direction. We call this the lay direction. The lay direction is equal or opposite the lay direction of strands around the core wire. There are two types: lang’s lay or regular lay.
Lang's lay
In lang’s lay, the lay direction of the strands and the wires in the strands are the same. The strands are closed around the core strand from bottom left to top right. Or vice versa. The wires are the same.
Characteristics:
- Has a tendency to rotate outward.
- Only suitable for situations where the ends have a fixed, non-rotation attachment point and the load cannot rotate. For example, counterweights at locks.
- With a lang’s lay rope, the outer wire lies on the surface over a longer length, which reduces the surface pressure. Under the right conditions, this extends the life span.
Regular lay
In the regular lay, the lay direction of the strands is opposite to the lay direction of the wires in the strands. The strands are closed around the core wire from bottom right to top left. The strands from bottom left to top right. The other way around is also possible.
Characteristics:
- Rotates out less than a lang’s lay wire rope.
- More resistant to distortion than a lang’s lay wire rope.
- A regular lay wire rope is more resistant to external influences, such as destruction or damage.
Materials
A wire rope can consist of different types of material.
- Uncoated steel wire rope
Wire ropes that have a relatively short life span (less than a year) and generally need to be discarded (replaced) because of damage can be made with uncoated material. Uncoated wire ropes are not always in stock.
- Galvanized steel wire rope
The biggest advantage of galvanized steel wire is its better resistance to corrosion. The zinc extends the life span of the wire rope in humid and corrosive environments. In addition, zinc also has a lubricating effect.
- Stainless steel wire rope
Stainless steel wire is highly resistant to corrosion and heat up to approximately 250°C. However, the resistance to fatigue is considerably less than that of uncoated and galvanized steel wires.
- Plastic-coated core
In some steel wire ropes, the core is coated with a plastic layer. The advantage: it lowers the wear between the core and the outer strands. This construction is also more stable, and a cable with a plastic-coated core has a high resistance to rotation around the axis as a result of a deflection angle.
- Compacted strands
There are also steel cables with compacted strands. These strands have a high filler factor, as the spaces between the strands are filled as much as possible during manufacturing. A compacted cable has a higher breaking load and an increased resistance to destruction and chafing. However, the cable is stiffer and has a lower resistance to fatigue at lower loads.
- Swaged wire rope
A swaged wire rope is rounder than other ropes. As a result, a swaged rope has a better bearing surface and an increased breaking load.
Let us advise you
As you can see, just behind the composition of a steel wire rope is a world of variation. Curious about which steel wire rope is suitable for your application? Let us inform you. At Mennens, we have years of knowledge and expertise.
Read more
Knowledge articles
Discover the main concerns of steel wire ropes:
- The origins of steel wire rope
- Wire rope end fittings
- Breaking load, usage rate & workload
- How corrosion affects steel wire ropes
Projects
Read experiences from organizations:
Services
Discover how Mennens can support you:





